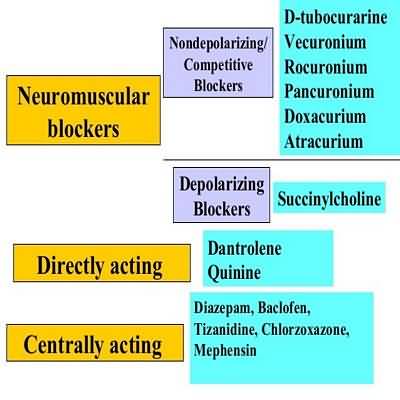
Nondepolarizing NeuromuscularJunction Blockers
Nondepolarizing NeuromuscularJunction Blockers
NMJ blockers interfere with neuromuscular transmission and cause flaccid paralysis by blocking acetylcholine receptors at the skeletal neuromuscular junction.
Indications
Adjuncts to general anesthetics to facilitate endotracheal intubation and relax skeletal muscle; to relax skeletal muscle to facilitate mechanical ventilation Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to NMJ blockers and the bromide ion. Use cautiously with myasthenia gravis; preg nancy (teratogenic in preclinical studies; may be used in cesarean section, but reversal may be difficult if patient has received magnesium sulfate to manage preeclampsia); renal or hepatic disease, respiratory depression, altered fluid or electrolyte balance; patients in whom an increase in heart rate may be dangerous. Adverse effects
CV: Increased heart rate Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, especially rash Musculoskeletal: Profound and prolonged muscle paralysis Respiratory: Depressed respiration, apnea,bronchospasm Interactions
Drug-drug Increased intensity and duration of neuromuscular block with some anes- thetics (isoflurane, enflurane, halothane, diethyl ether), some parenteral antibiotics (aminoglycosides, clindamycin, lincomycin, bacitracin, polymyxin B), ketamine, quinine, quinidine, calcium channel-blocking drugs (eg, verapamil), Mg2+salts, and in hypokalemia (from K+-depleting diuretics) Decreased intensity of neuromuscular block with acetylcholine, cholinesterase inhibitors, K+salts, theophyllines, phenytoins, azathioprine, mercaptopurine, carbamazepine Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Hypersensitivity to NMJ blockers and the bromide ion, myasthenia gravis, pregnancy, renal or hepatic disease, respiratory depression, altered fluid or electrolyte balance Physical: Weight, T, skin condition, hydration, reflexes, bilateral grip strength, pulse, BP, R and adventitious sounds, LFTs, renal function tests, serum electrolytes Interventions
Black box
warning Drug should be given only by trained personnel (anesthesiologists); intubation will be necessary. Arrange to have facilities on standby to maintain airway and provide mechanical ventilation. Provide neostigmine, pyridostigmine, or edrophonium (cholinesterase inhibitors) on standby to overcome excessive neuromuscular block. Provide atropine or glycopyrrolate on standby to prevent parasympathomimetic effects of cholinesterase inhibitors. Provide a peripheral nerve stimulator on standby to assess degree of neuromuscular block, as needed. Change patientís position frequently, and provide skin care to prevent decubitus ulcer formation when drug is used for other than brief periods. Monitor conscious patient for pain or distress that he may not be able to communicate. Reassure conscious patients frequently. Teaching points
Teaching points
about what these drugs do and how the patient will feel should be incorporated into the overall teaching program about the procedure. Adverse effects
in italics are most common; those in bold are life-threatening. U Do not crush. Representative drugs
atracurium cisatracurium pancuronium rocuronium vecuronium