Nonsteroidal
Nonsteroidal
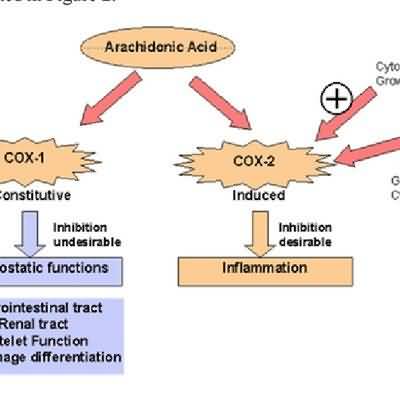
NSAIDs have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities largely related to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis; exact mechanisms of action are not known.
Indications
Relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and juvenile arthritis Relief of mild to moderate pain Treatment of primary dysmenorrhea Fever reduction Reduction of number of adenomatous colorectal polyps in adults with familial adenomatous polyposis Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with allergy to salicylates or other NSAIDs (more common in patients with rhinitis, asthma, chronic urticaria, nasal polyps); CV dysfunction, hypertension; peptic ulceration, GI bleeding; pregnancy or lactation. Use cautiously with impaired hepatic function, impaired renal function, heart failure. Adverse effects
CNS: Headache, dizziness, somnolence, insomnia,fatigue, tiredness, tinnitus, ophthalmologic effects Dermatologic: Rash,pruritus, sweating, dry mucous membranes, stomatitis GI: Nausea, dyspepsia, GI pain,diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, flatulence GU: Dysuria, renal impairment Hematologic: Bleeding, platelet inhibition with higher doses, neutropenia, eosinophilia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytope- nia, agranulocytosis, granulocytopenia, aplastic anemia, decreased Hgb or Hct, bone marrow depression, menorrhagia Respiratory: Dyspnea, hemoptysis, pharyngitis, bronchospasm, rhinitis Other: Peripheral edema, anaphylactoid reactions to anaphylactic shock Interactions
Drug-drug Increased toxic effects of lithium with NSAIDs Decreased diuretic effect with loop diuretics: bumetanide, furosemide, ethacrynic acid Potential decrease in antihypertensive effect of beta-adrenergic blockers Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Allergy to salicylates or other NSAIDs; CV dysfunction, hypertension; peptic ulceration, GI bleeding; impaired hepatic function; impaired renal function; pregnancy; lactation Physical: Skin color, lesions; T; orientation, reflexes, ophthalmologic evaluation, audiometric evaluation, peripheral sensa- tion; P, BP, edema; R, adventitious sounds; liver evaluation, bowel sounds; CBC, clotting times, urinalysis, LFTs, renal function tests, serum electrolytes, stool guaiac Interventions
Black box
warning Monitor patient for CV events, GI bleed; risk may be increased. Administer drug with food or after meals if GI upset occurs. Establish safety measures if CNS, visual disturbances occur. Arrange for periodic ophthalmologic examination during long-term therapy. Arrange for discontinuation of drug if eye changes, symptoms of hepatic impairment, renal impairment occur. Institute emergency procedures if overdose occurs (gastric lavage, induction of emesis, supportive therapy). Provide comfort measures to reduce pain and to reduce inflammation. Provide frequent small meals if GI upset is severe. Teaching points
Use these drugs only as suggested. Do not exceed the prescribed dosage. Take these drugs with food or after meals if GI upset occurs. Avoid over-the-counter drugs while taking these drugs. Many of these drugs contain similar medications; serious overdosage can occur. If you feel you need one of these preparations, consult your health care provider. Avoid alcohol while taking these drugs. You may experience these side effects: Nausea, GI upset, dyspepsia (take with food); diarrhea or constipation; drowsiness, dizziness, vertigo, insomnia (use caution when driving or operating dangerous machinery). Report sore throat, fever, rash, itching, weight gain, swelling in ankles or fingers, changes in vision, black or tarry stools. Representative drugs
celecoxib diclofenac diflunisal etodolac fenoprofen flurbiprofen ibuprofen indomethacin ketoprofen ketorolac mefenamic acid meloxicam nabumetone naproxen oxaprozin piroxicam sulindac tolmetin