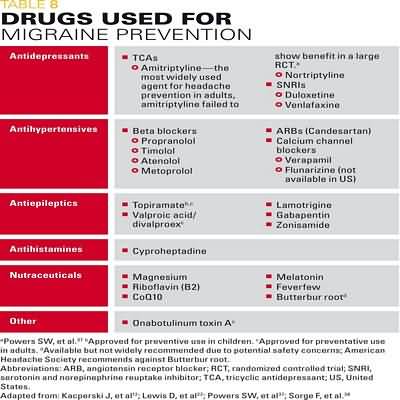
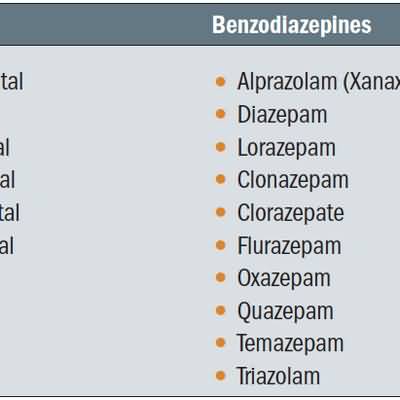
Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones are antibacterial. They interfere with DNA replication in susceptible gram-negative bacteria, preventing cell reproduction and leading to death of bacteria.
Indications
Treatment of infections caused by susceptible gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia rettgeri, Mor- ganella morganii, Pseudomonas aerug- inosa, Citrobacter freundii, Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, group D streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae Unlabeled use: Treatment of patients with cystic fibrosis who have pulmonary exacerbations Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with allergy to any fluoroquinolone, pregnancy, lactation, history of myasthenia gravis. Use cautiously with renal impairment, seizures. Adverse effects
CNS: Headache, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, somnolence, depression, blurred vision GI: Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, diarrhea,abdominal pain Hematologic: Elevated BUN, AST, ALT, serum creatinine and alkaline phosphatase; decreased WBC, neutrophil count, Hct Other: Fever, rash, photosensitivity,QTinterval prolongation, tendinitis, tendon rupture Interactions
Drug-drug Decreased therapeutic effect with iron salts, sucralfate Decreased absorption with antacids Increased serum levels and toxic effects of theophyllines with fluoroquinolones Risk of prolonged QT interval if combined with other drugs that prolong QT interval Assessment
History: Allergy to fluoroquinolones, renal impairment, seizures, lactation Physical: Skin color, lesions; T; orientation, reflexes, affect; mucous membranes, bowel sounds; LFTs, renal function tests Interventions
Black box
warning Drug increases risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture, especially in older patients, patients with organ transplants, and patients on corticosteroids; may exacerbate weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis. Avoid use in these patients. Arrange for culture and sensitivity tests before beginning therapy. Continue therapy for 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared. Administer oral drug 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals with a glass of water. Ensure that patient is well hydrated during course of drug therapy. Administer antacids, if needed, at least 2 hr after dosing. Monitor clinical response; if no improvement is seen or a relapse occurs, repeat culture and sensitivity. Ensure ready access to bathroom if diarrhea occurs. Arrange for appropriate bowel training program if constipation occurs. Provide frequent small meals if GI upset occurs. Arrange for monitoring of environment (noise, temperature) and analgesics, for headache. Establish safety precautions if CNS, visual changes occur. Encourage patient to complete full course of therapy. Teaching points
Take oral drugs on an empty stomach, 1hour before or 2 hours after meals. If you need an antacid, do not take it within 2 hours of ciprofloxacin dose. Drink plenty of fluids. You may experience these side effects: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain (frequent small meals may help); diarrhea or constipation (consult your health care provider); drowsiness, blurring of vision, dizziness (observe caution if driving or using hazardous equipment). Report rash, visual changes, severe GI problems, weakness, tremors. Representative drugs
ciprofloxacin gemifloxacin levofloxacin moxifloxacin norfloxacin ofloxacin