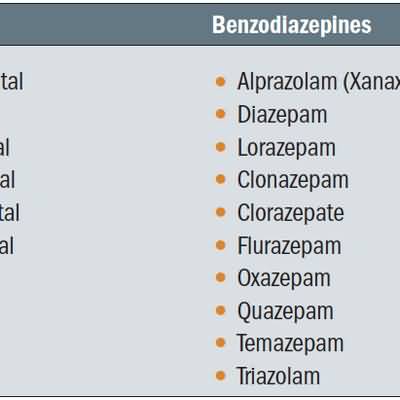
Antiviral
Antiviral
Antiviral drugs inhibit viral DNA or RNA replication in the virus, preventing replication and leading to viral death.
Indications
Initial and recurrent mucosal and cutaneous HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections in immunocompromised patients, encephalitis, herpes zoster HIV infections (part of combination therapy) Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis in patients with AIDS Severe initial and recurrent genital herpes infections Treatment and prevention of influenza A respiratory tract illness Prevention of CMV infection in patients receiving kidney, heart, or pancreas transplant who are considered at high risk for CMV infection Treatment of initial HSV genital infections and limited mucocutaneous HSV infections in immunocompromised patients (ointment) Unlabeled uses: Treatment of herpes zoster, CMV and HSV infection following transplant, herpes simplex infections, infectious mononucleosis, varicella pneumonia, and varicella zoster in immunocompromised patients Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with allergy to drug, seizures, heart failure, renal disease, lactation. Adverse effects
Systemic administration CNS: Headache, vertigo, depression, tremors, encephalopathic changes, fatigue Dermatologic: Inflammation or phlebitis at injection sites,rash, hair loss, sweating GI: Nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, anorexia, taste perversion GU: Crystalluria with rapid IV administration, hematuria Metabolic:Hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia Topical administration Skin:Transient burning at the site of application Antivirals 30 ? Antivirals Adverse effects
in italics are most common; those in bold are life-threatening. U Do not crush. Interactions
Drug-drug Increased drug effects with probenecid Increased nephrotoxicity with other nephrotoxic drugs ?Drug-alternative therapy Decreased effectiveness if combined with St. Johnís Wort Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Allergy to drug, seizures, heart failure, renal disease, lactation Physical: Skin color, lesions; orientation; BP, P, auscultation, perfusion, edema; R, adventitious sounds; urinary output; BUN, creatinine clearance Interventions
Systemic administration Ensure that the patient is well hydrated with IV or PO fluids. Provide support and encouragement to deal with disease. Provide frequent small meals if systemic therapy causes GI upset. Provide skin care, analgesics if needed for rash. Topical administration Start treatment as soon as possible after onset of signs and symptoms. Wear a rubber glove or finger cot when applying drug. Teaching points
Systemic administration Complete the full course of oral therapy, and do not exceed the prescribed dose. These drugs are not a cure for your disease but they should make you feel better. Avoid sexual intercourse if lesions are visible. You may experience these side effects: Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, headache, dizziness. Report difficulty urinating, skin rash, increased severity or frequency of recurrences. Topical administration Wear rubber gloves or finger cots to apply the drug to prevent autoinoculation of other sites and transmission of the disease. These drugs do not cure the disease; applying the drug during symptom-free periods will not prevent recurrences. Avoid sexual intercourse while visible lesions are present. These drugs may cause burning, stinging, itching, rash; notify your health care provider if these are pronounced. Representative drugs
abacavir acyclovir acyclovir sodium adefovir amantadine atazanavir boceprevir cidofovir darunavir delavirdine didanosine docosanol efavirenz emtricitabine entecavir etravirine famciclovir fosamprenavir foscarnet ganciclovir imiquimod indinavir lamivudine lopinavir maraviroc nelfinavir nevirapine oseltamivir penciclovir peramivir raltegravir ribavirin rilpivirine rimantadine ritonavir saquinavir sinecatechins stavudine telaprevir telbivudine tenofovir tipranavir trifluridine valacyclovir valganciclovir zanamivir zidovudine