Opioids
Opioids
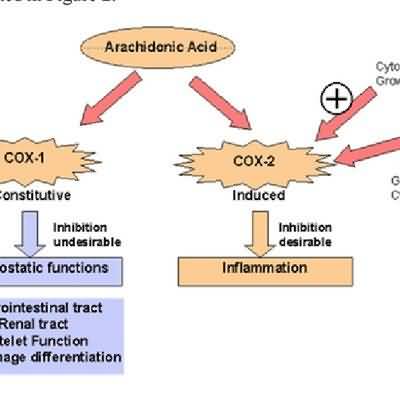
Opioids act as agonists at specific opioid receptors in the CNS to produce analgesia, euphoria, sedation; the receptors mediating these effects are thought to be the same as those mediating the effects of endogenous opioids (enkephalins, endorphins).
Indications
Relief of moderate to severe acute and chronic pain Preoperative medication to sedate and allay apprehension, facilitate induction of anesthesia, and reduce anesthetic dosage Analgesic adjunct during anesthesia Intraspinal use with microinfusion devices for the relief of intractable pain Unlabeled use: Relief of dyspnea associated with acute left ventricular failure and pulmonary edema Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to opioids, diarrhea caused by poisoning until toxins are eliminated, during labor or delivery of a preterm infant (may cross immature blood–brain barrier more readily), after biliary tract surgery or following surgical anastomosis, pregnancy, or labor (can cause respiratory depression of neonate; may prolong labor). Use cautiously with head injury and increased intracranial pressure; acute asthma, COPD, cor pulmonale, preexisting respiratory depression, hypoxia, hypercapnia (may decrease respiratory drive and increase airway resistance); lactation (may be safer to wait 4–6 hr after administration to nurse the baby); acute abdominal conditions; CV disease, supraventricular tachycardias; myxedema; seizure disorders; acute alcoholism, delirium tremens; cerebral arteriosclerosis; ulcerative colitis; fever; kyphoscoliosis; Addison’s disease; prostatic hypertrophy, urethral stricture; recent GI or GU surgery; toxic psychosis; renal or hepatic impairment. Adverse effects
CNS: Light-headedness, dizziness, sedation, euphoria, dysphoria, delirium, in- somnia, agitation, anxiety, fear, hallucinations, disorientation, drowsiness, lethargy, impaired mental and physical performance, coma, mood changes, weakness, headache, tremor, seizures, miosis, visual disturbances, suppression of cough reflex CV: Facial flushing, peripheral circulatory collapse, tachycardia, bradycardia, arrhythmia, palpitations, chest wall rigidity, hypertension, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, syncope Adverse effects
in italics are most common; those in bold are life-threatening. U Do not crush. Dermatologic: Pruritus, urticaria, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, edema GI: Nausea, vomiting,dry mouth, anorexia, constipation, biliary tract spasm; increased colonic motility in patients with chronic ulcerative colitis GU: Ureteral spasm, spasm of vesical sphincters, urinary retention or hesitancy, oliguria, antidiuretic effect, reduced libido or potency Local: Tissue irritation and induration (subcutaneous injection) Major hazards:Respiratory depression, apnea, circulatory depression, respiratory arrest, shock, cardiac arrest Other: Sweating, physical tolerance and dependence, psychological dependence Interactions
Drug-drug Increased likelihood of respiratory depression, hypotension, profound sedation, or coma in patients receiving barbiturate general anesthetics ?Drug-lab test Elevated biliary tract pressure (an effect of opioids) may cause increases in plasma amylase, lipase; determinations of these levels may be unreliable for 24 hr Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Hypersensitivity to opioids; diarrhea caused by poisoning; labor or delivery of a premature infant; biliary tract surgery or surgical anastomosis; head injury and increased intracranial pressure; acute asthma, COPD, cor pulmonale, preexisting respiratory depression, hypoxia, hypercapnia; acute abdominal conditions; CV dis- ease, supraventricular tachycardias; myxedema; seizure disorders; acute alcoholism, delirium tremens; cerebral arteriosclerosis; ulcerative colitis; fever; kyphoscoliosis; Addison’s disease; prostatic hypertrophy; urethral stricture; recent GI or GU surgery; toxic psychosis; renal or hepatic impairment; pregnancy; lactation Physical: T; skin color, texture, lesions; orientation, reflexes, bilateral grip strength, affect; P, auscultation, BP, orthostatic BP, perfusion; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output; urinary frequency, voiding pattern, normal output; ECG; EEG; LFTs, thyroid and renal function tests Interventions
Caution patient not to chew or crush controlled-release preparations. Dilute and administer IV slowly to minimize likelihood of Adverse effects
. Direct patient to lie down during IV administration. Keep opioid antagonist and equipment for assisted or controlled respiration readily available during IV administration. Use caution when injecting IM or subcutaneously into chilled areas or in patients with hypotension or in shock; impaired perfusion may delay absorption; with repeated doses, an excessive amount may be absorbed when circulation is restored. Monitor injection sites for irritation, extravasation. Instruct postoperative patients in pulmonary toilet; drug suppresses cough reflex. Monitor bowel function and arrange for anthraquinone laxatives for severe constipation. Institute safety precautions (use side rails, as- sist with walking) if CNS, vision effects occur. Provide frequent small meals if GI upset occurs. Control environment if sweating, visual difficulties occur. Provide back rubs, positioning, and other nondrug measures to alleviate pain. Reassure patient about addiction liability; most patients who receive opioids for med- ical reasons do not develop dependence syn- dromes. Teaching points
When these drugs are used as a preoperative medication, teach the patient about the drug when explaining the procedure. Take these drugs exactly as prescribed. Avoid alcohol, antihistamines, sedatives, tranquilizers, and over-the-counter drugs. Do not take any leftover medication for other disorders, and do not let anyone else take your prescription. You may experience these side effects: Nausea, loss of appetite (take the drug with food and lie quietly); constipation (notify your health care provider if this is severe; a laxative may help); dizziness, sedation, drowsiness, impaired visual acuity (avoid driving or performing other tasks requiring alertness, visual acuity). Report severe nausea, vomiting, constipation, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, skin rash. Representative drugs
alfentanil buprenorphine butorphanol codeine fentanyl hydrocodone hydromorphone levorphanol meperidine methadone morphine sulfate nalbuphine opium oxycodone oxymorphone pentazocine sufentanil tapentadol tramadol