Penicillins
Penicillins
Penicillins are antibiotics. They are bactericidal, inhibiting the synthesis of cell wall of sensitive organisms, causing cell death in susceptible organisms.
Indications
Treatment of moderate to severe infections caused by sensitive organisms: streptococci, pneumococci, staphylococci, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Treponema pallidum,men- ingococci, Actinomyces israelii, Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium tetani, Leptotrichia buccalis (Vincent’s disease), Spirillum minusor Streptobacillus moniliformis, Listeria monocytogenes, Pas- teurella multocida, Erysipelothrix insidiosa, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Alcaligenes faecalis, Salmonella, Shigella, Proteus mirabilis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Bacillus anthracis Treatment of syphilis, gonococcal infections Unlabeled use: Treatment of Lyme disease Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with allergy to penicillins, cephalosporins, other allergens. Use cautiously with renal disease, pregnancy, lactation (may cause diarrhea or candidiasis in the infant). Adverse effects
CNS: Lethargy, hallucinations, seizures GI: Glossitis, stomatitis, gastritis, sore mouth,furry tongue, black “hairy” tongue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, enterocolitis, pseudomembranous colitis, nonspecific hepatitis GU: Nephritis-oliguria, proteinuria, hematuria, casts, azotemia, pyuria Hematologic: Anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, prolonged bleeding time Hypersensitivity: Rash, fever, wheezing, anaphylaxis Local: Pain, phlebitis, thrombosis at injection site, Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction when used to treat syphilis Other: Superinfections,sodium overload, leading to heart failure Interactions
Drug-drug Decreased effectiveness with tetracyclines Inactivation of parenteral aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, streptomycin, tobramycin) if mixed in the same solution Risk of increased serum levels if combined with aspirin, indomethacin, diuretics, sulfonamides ?Drug-lab test False-positive Coombs’ test (IV) Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Allergy to penicillins, cephalosporins, other allergens, renal disease, lactation Physical: Culture infected area; skin rashes, lesions; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output; CBC, LFTs, renal function tests, serum electrolytes, Hct, urinalysis; skin test with benzylpenicilloylpolylysine if hypersensitivity reactions have occurred Adverse effects
in italics are most common; those in bold are life-threatening. U Do not crush. Interventions
Culture infected area before beginning treatment; reculture area if response is not as expected. Use the smallest dose possible for IM injection to avoid pain and discomfort. Arrange to continue treatment for 48–72 hr after the patient becomes asymptomatic. Monitor serum electrolytes and cardiac sta- tus if penicillin G is given by IV infusion. Na or K preparations have been associated with severe electrolyte imbalances. Check IV site carefully for signs of throm- bosis or local drug reaction. Do not give IM injections repeatedly in the same site; atrophy can occur. Monitor in- jection sites. Explain the reason for parenteral routes of administration; offer support and encour- agement to deal with therapy. Provide frequent small meals if GI upset occurs. Arrange for comfort and treatment measures for superinfections. Provide for frequent mouth care if GI effects occur. Ensure that bathroom facilities are readily available if diarrhea occurs. Keep epinephrine, IV fluids, vasopressors, bronchodilators, oxygen, and emergency equipment readily available in case of serious hypersensitivity reaction. Arrange for the use of corticosteroids, antihistamines for skin reactions. Teaching points
You may experience these side effects: Upset stomach, nausea, vomiting (eat frequent small meals); sore mouth (provide frequent mouth care); diarrhea; pain or discomfort at the injection site (report if very uncomfortable). Report unusual bleeding, sore throat, rash, hives, fever, severe diarrhea, difficulty breathing. Representative drugs
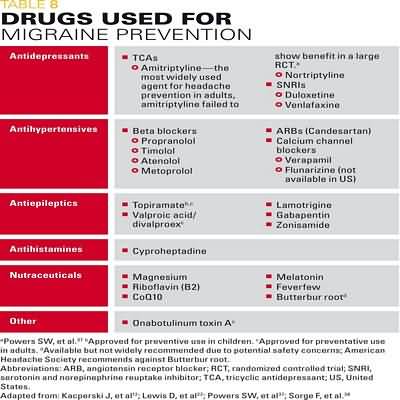
amoxicillin ampicillin oxacillin penicillin G benzathine penicillin G potassium penicillin G procaine penicillin V piperacillin