Tetracyclines
Tetracyclines
Tetracyclines are antibiotics. They are bacteriostatic; inhibit protein synthesis of susceptible bacteria, preventing cell replication.
Indications
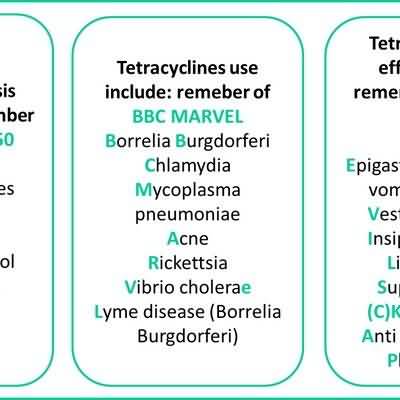
Treatment of infections caused by rickettsiae; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; agents of psittacosis, ornithosis, lymphogranuloma venereum, and granuloma inguinale; Borrelia recurrentis, Haemophilus ducreyi, Pasteurella pestis, Pasteurella tularensis, Bartonella bacilliformis, Bacteroides, Vibrio comma, Vibrio fetus, Brucella, Escherichia coli, Escherichia aerogenes, Shigella, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Diplococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella
when penicillin is contraindicated, infections caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Listeria monocytogenes, Treponema pallidum, Treponema pertenue, Clostridium, Bacillus anthracis, Actinomyces, Fusobacterium fusiforme, Neisseria meningitidis Adjunct to amebicides in acute intestinal amebiasis Treatment of malaria Treatment of anthrax Treatment of acne Treatment of complicated urethral, endocervical, or rectal infections in adults caused by Chlamydia trachomatis Treatment of superficial ocular infections caused by susceptible strains of microorganisms Prophylaxis of ophthalmia neonatorum caused by N. gonorrhoeaeor C. trachomatis Unlabeled uses: Lyme disease, endocarditis, facial nerve paralysis, arthritis, early syphilis, chlamydial infection, PID, epididymitis, prophylaxis after sexual assault Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with allergy to any tetracyclines, allergy to tartrazine (in 250-mg tetracycline capsules marketed under brand name Sumycin), pregnancy (toxic to fetus), lactation (causes damage to the teeth of infants). Use cautiously with hepatic or renal impairment; ocular viral, mycobacterial, or fungal infections. Adverse effects
Dermatologic: Phototoxic reactions, rash,exfoliative dermatitis GI: Discoloring and inadequate calcification of primary teeth of fetus if used by pregnant women, discoloring and inadequate calcification of permanent teeth if used during period of dental development, fatty liver, hepatic failure, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, dysphagia, enterocolitis, esophageal ulcers Hematologic: Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, eosinophilia, leukocytosis, leukopenia Hypersensitivity: Reactions from urticaria to anaphylaxis, including intracranial hypertension Local: Transient irritation, stinging, itching, angioneurotic edema, urticaria, dermatitis, superinfections with ophthalmic or dermatologic use Other: Superinfections,local irritation at parenteral injection sites Interactions
Drug-drug Decreased absorption with calcium salts, magnesium salts, zinc salts, aluminum salts, bismuth salts, iron, urine alkalinizers, food, dairy products, charcoal Increased digoxin toxicity Decreased effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives (rare) with a risk of breakthrough bleeding or pregnancy Decreased activity of penicillins Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Allergy to any of the tetracyclines; allergy to tartrazine; hepatic or renal impairment, pregnancy, lactation; ocular viral, mycobacterial, or fungal infections Physical: Site of infection, skin color, lesions; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, output, liver evaluation; urinalysis, BUN, LFTs, renal function tests Interventions
Administer oral medication on an empty stomach, 1 hr before or 2–3 hr after meals. Do not give with antacids. If antacids must be used, give them 3 hr after the dose of tetracycline. Culture infected area prior to drug therapy. Do not use outdated drugs; degraded drug is highly nephrotoxic and should not be used. Do not give oral drug with meals, antacids, or food. Provide frequent hygiene measures if superinfections occur. Protect patient from sunlight and bright lights if photosensitivity occurs. Arrange for regular renal function tests if long-term therapy is used. Use topical preparations of this drug only when clearly indicated. Sensitization from the topical use of this drug may preclude its later use in serious infections. Topical preparations containing antibiotics that are not ordinarily given systemically are preferable. Teaching points
Systemic administration Take these drugs throughout the day for best results. These drugs should be taken on an empty stomach, 1 hour before or 2–3 hours after meals, with a full glass of water. Do not take these drugs with food, dairy products, iron preparations, or antacids. Take the full course of therapy prescribed; if any drug is left, discard it immediately. Never take an outdated product. Pregnancy may occur when taking tetracycline with hormonal contraceptives. To be sure of avoiding pregnancy, use an additional type of contraceptive while using this drug. Report severe cramps, watery diarrhea, rash or itching, difficulty breathing, dark urine or light-colored stools, yellowing of the skin or eyes. Eyedrop administration To give eyedrops: Lie down or tilt your head backward and look at the ceiling. Drop suspension drug inside your lower eyelid while looking up. Close your eye, and apply gentle pressure to the inner corner of the eye for 1 minute.
Apply ointment inside the lower eyelid; close your eyes, and roll your eyeball in all directions. These drugs may cause temporary blurring of vision or stinging after application. Notify your health care provider if stinging or itching becomes severe. Take the full course of therapy prescribed; discard any leftover medication. Apply dermatologic solution until skin is wet; avoid eyes, nose, and mouth. Topical administration You may experience transient stinging or burning; this will subside quickly; skin in the treated area may become yellow; this will wash off. Use cosmetics as you usually do. Adverse effects
in italics are most common; those in bold are life-threatening. U Do not crush. Wash area before applying (unless contraindicated); this drug may stain clothing. You may experience these side effects: Stomach upset, nausea; superinfections in the mouth, vagina (frequent washing may help; if it becomes severe, medication may help); sensitivity of the skin to sunlight (use protective clothing and sunscreen). Report worsening of condition, rash, irritation. Representative drugs
demeclocycline doxycycline minocycline tetracycline