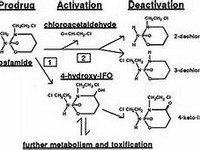
Lenalidomide
Lenalidomide
CLINICAL USE
Treatment of multiple myeloma in combination with dexamethasoneDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
25 mg daily on days 1–21 of a 28 day cycle; reduce dose if patient has neutropenia or thrombocytopenia; see data sheetPHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
30–50 10 mg daily, increasing to 15 mg after 2 cycles if patient is not responding<30 15 mg every 48 hoursDOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsCardiac glycosides: possibly increases concentration of digoxinADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
OralRate of Administration
–Comments
–OTHER INFORMATION
May cause acute renal failure – monitor renal function during treatment. Patients with renal impairment are more likely to develop side effects
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home