Bortezomib
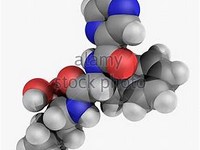
Bortezomib
CLINICAL USE
Treatment of multiple myeloma for people who have already tried at least 2 prior therapies and have disease progression
DOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
1.3 mg/m2 twice weekly for 2 weeks (days 1, 4, 8 and 11) followed by a 10-day rest period
PHARMACOKINETICS
Molecular weight :384.2 %Protein binding :82.9 %Excreted unchanged in urine : Small amount Volume of distribution (L/kg) :>500 litreshalf-life – normal/ESRD (hrs) :5–15/unknown DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
30–50 Dose as in normal renal function 10–30 Dose as in normal renal function. Monitor carefully. <10 : A reduced dose may be required. Monitor carefully DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
CAPD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/min HD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/minHDF/high flux :Unknown dialysability. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/minCAV/VVHD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR=10–30 mL/min IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsNone known ADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
3.5 mL sodium chloride 0.9% Route
IV bolus Rate of Administration
3 to 5 seconds Comments
Administer within 8 hours of reconstitution OTHER INFORMATION
Consecutive doses should be at least 72 hours apartNormal doses have been used in patients with a GFR of 10–30 mL/min but there is an increased risk of adverse effects. (Jagannath S, Barlogie B, Berenson JR, et al. Bortezomib in recurrent and/or refractory multiple myeloma. Cancer. 2005; 103(6): 1195–1200)Some trials have used doses of 1 mg/m 2 in patients with a GFR of 10–30 mL/min, with similar efficacy and incidence of side effectsBoth hypo- and hyperkalaemia have been reported with bortezomib as has hypophosphataemia and hypomagnesaemiaThere have been incidences of renal impairment, renal colic, proteinuria, dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary hesitation and haematuriaAnecdotally, has been used at normal doses in a few haemodialysis patients; in some of the patients platelet infusions have been requiredIn patients with peripheral neuropathy then bortezomib has a high probability of exacerbating it.
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home