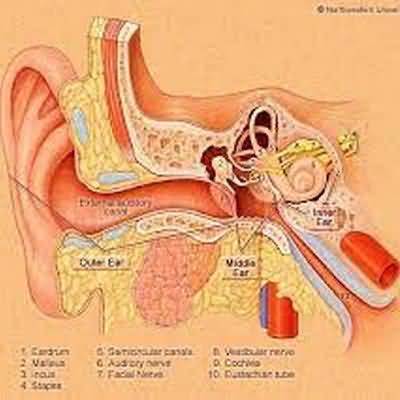
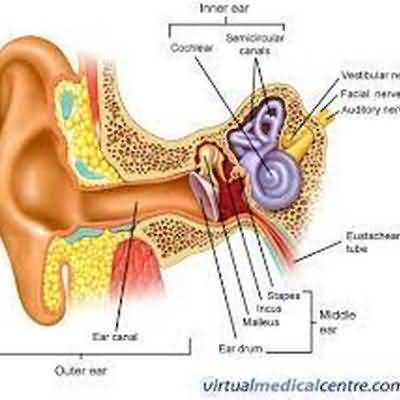
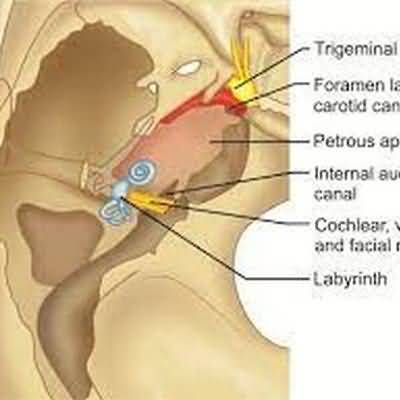
Evaluation of Hearing
Evaluation of Hearing
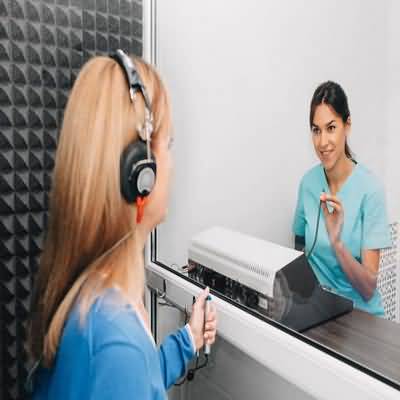
In a quiet room, the hearing level may be estimated by having the patient repeat aloud words presented in a soft whisper, a normal spoken voice, or a shout
A 512-Hz tuning fork is useful in differentiating conductive from sensorineural losses
In the Weber test, the tuning fork is placed on the forehead or front teeth
In conductive losses, the sound appears louder in the poorer-hearing ear, whereas in sensorineural losses it radiates to the better side
In the Rinne test, the tuning fork is placed alternately on the mastoid bone and in front of the ear canal
In conductive losses greater than 25 dB, bone conduction exceeds air conduction; in sensorineural losses, the opposite is true
Formal audiometric studies are performed in a soundproofed room