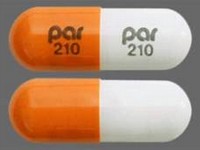
Loperamide

Loperamide
CLINICAL USE
Antidiarrhoeal agentDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
4 mg stat, then 2 mg after each loose stool; maximum 16 mg dailyPHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
OralRate of Administration
–Comments
–OTHER INFORMATION
In normal doses loperamide may cause excessive drowsiness in CKD 5
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home