sigmoid sinus thrombosis
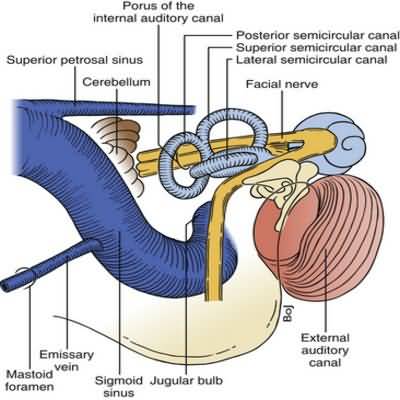
sigmoid sinus thrombosis
Trapped infection within the mastoid air cells adjacent to the sigmoid sinus may cause septic thrombophlebitis
This is heralded by signs of systemic sepsis (spiking fevers, chills), at times accompanied by signs of increased intracranial pressure (headache, lethargy, nausea and vomiting, papilledema)
Diagnosis can be made noninvasively by magnetic resonance venography (MRV)
Primary treatment is with intravenous antibiotics (based on culture results)
Surgical drainage with ligation of the internal jugular vein may be indicated when embolization is suspected