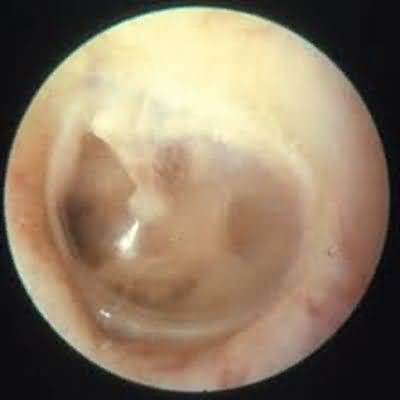
serous otitis media
serous otitis media
ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS
Prolonged eustachian tube dysfunction with resultant negative middle ear pressure may cause a transudation of fluid
In adults, serous otitis media usually occurs with an upper respiratory tract infection, with barotrauma, or with chronic allergic rhinitis, but when persistent and unilateral, nasopharyngeal carcinoma must be excluded
The tympanic membrane is dull and hypomobile, occasionally accompanied by air bubbles in the middle ear and conductive hearing loss
The treatment of serous otitis media is similar to that for eustachian tube dysfunction
When medication fails to bring relief after several months, a ventilating tube placed through the tympanic membrane may restore hearing and alleviate the sense of aural fullness
Endoscopically guided laser expansion of the nasopharyngeal orifice of the eustachian tube or balloon dilation may improve function in recalcitrant cases