otologic manifestations of aids
otologic manifestations of aids
The otologic manifestations of AIDS are protean
The pinna and external auditory canal may be affected by Kaposi sarcoma and by persistent and potentially invasive fungal infections (particularly Aspergillus fumigatus)
Serous otitis media due to eustachian tube dysfunction may arise from adenoidal hypertrophy (HIV lymphadenopathy), recurrent mucosal viral infections, or an obstructing nasopharyngeal tumor (eg, lymphoma)
Unfortunately, ventilating tubes are seldom helpful and may trigger profuse watery otorrhea
Acute otitis media is usually caused by typical bacterial organisms, including Proteus, Staphylococcus, and Pseudomonas, and rarely, by Pneumocystis jirovecii
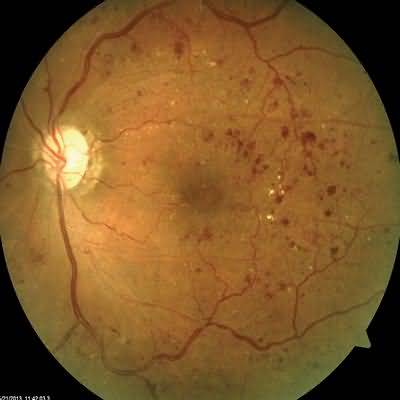
Sensorineural hearing loss is common and, in some cases, results from viral CNS infection
In cases of progressive hearing loss, cryptococcal meningitis and syphilis must be excluded
Acute facial paralysis due to herpes zoster infection (Ramsay Hunt syndrome) occurs commonly and follows a clinical course similar to that in nonimmunocompromised patients
Treatment
is with high-dose acyclovirCorticosteroids may also be effective as an adjunct