hearing loss conductive and sensorineural
hearing loss conductive and sensorineural
Most commonly due to cerumen impaction, transient eustachian tube dysfunction from upper respiratory tract infection, or age-related hearing loss
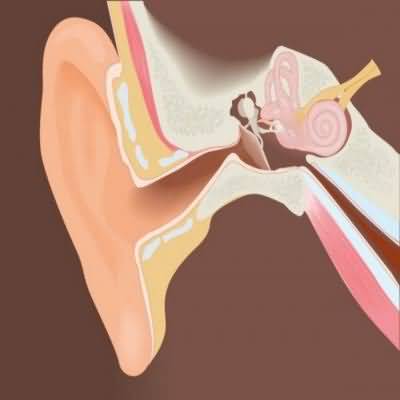
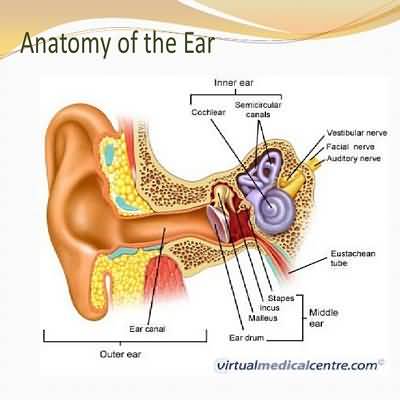
Four mechanisms each result in impairment of the passage of sound vibrations to the inner ear:
Conductive losses in adults are most commonly due to cerumen impaction or transient eustachian tube dysfunction from upper respiratory tract infection
Persistent conductive losses usually result from chronic ear infection, trauma, or otosclerosis
Conductive hearing loss is often correctable with medical or surgical therapy, or both
B
Sensorineural Hearing Loss Sensory and neural causes of hearing loss are difficult to differentiate due to testing methodology, thus often referred to as “sensorineural
” Sensorineural hearing losses in adults are common