ACE inhibitors
ACE inhibitors
ACE inhibitors block ACE in the lungs from converting angiotensin I, activated when renin is released from the kidneys, to angiotensin II, a powerful vasoconstrictor. Blocking this conversion leads to decreased BP, decreased aldosterone secretion, a small increase in serum potassium levels, and sodium and fluid loss; increased prostaglandin synthesis also may be involved in the antihypertensive action.
Indications
Treatment of hypertension (alone or with thiazide type diuretics) Treatment of heart failure (used with diuretics and digitalis) Treatment of stable patients within 24 hr of acute MI to improve survival (lisinopril) Reduction in risk of MI, stroke, and death from CV causes (ramipril) Treatment of left ventricular dysfunction post-MI (captopril, trandolapril) Treatment of asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction (enalapril) Treatment of diabetic nephropathy (captopril) Unlabeled uses: Renovascular hypertension, nondiabetic nephropathy, migraine prophylaxis, stroke prevention, heart failure, high risk of CAD, diabetes, chronic renal disease, scleroderma renal crisis Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with allergy to the drug, impaired renal function, heart failure, salt or volume depletion, lactation, pregnancy, history of angioedema, bilateral renal artery stenosis. Adverse effects
CNS: Dizziness, headache, fatigue CV: Tachycardia, angina pectoris, MI, Raynaudís syndrome, heart failure, hypotension in salt or volume depleted patients Dermatologic: Rash,pruritus, alopecia, pemphigoid like reaction, scalded mouth sensation, exfoliative dermatitis, photosensitivity GI: Gastric irritation, aphthous ulcers,pep- tic ulcers, dysgeusia, cholestatic jaundice, hepatocellular injury, anorexia, constipation GU: Proteinuria, renal insufficiency, renal failure,polyuria, oliguria, urinary frequency Hematologic: Neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, pancytopenia, hyperkalemia Other: Cough,malaise, dry mouth, lymph- adenopathy, angioedema Interactions
Drug-drug Increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions with allopurinol Decreased anti- hypertensive effects with indomethacin Increased risk of hyperkalemia if combined with aldosterone blockers, potassium-sparing diuretics, aliskiren, cyclosporine, potassium supplements
Drug-food Decreased absorption of selected drugs if taken with food
Drug-lab test False positive test for urine acetone Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Allergy to ACE inhibitors, impaired renal function, heart failure, salt or volume depletion, pregnancy, lactation Physical: Skin color, lesions, turgor; T, P, BP, peripheral perfusion; mucous membranes; bowel sounds; liver evaluation; urinalysis, LFTs, renal function tests, CBC and differential, potassium levels Interventions
Black box
warning Ensure that patient is not pregnant before beginning therapy; serious fetal effects can occur. Administer 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals; is affected by food in GI tract (captopril, moexipril). Alert surgeon and mark patientís chart that ACE inhibitor is being taken; angiotensin II formation subsequent to compensatory renin release during surgery will be blocked; hy- potension may be reversed with volume ex- pansion. Monitor patient closely in situations that may lead to a fall in BP due to reduction in fluid volume (excessive perspiration and dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea) because excessive hypotension may occur. Arrange for reduced dosage in patients with impaired renal function. Arrange for bowel program if constipation occurs. Provide frequent small meals if GI upset is severe. Provide frequent mouth care and oral hygiene if mouth sores, alteration in taste occur. Caution patient to change position slowly if orthostatic changes occur. Provide skin care as needed. Teaching points
Take these drugs 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals; do not take with food (captopril, moexipril). Do not stop taking the medication without consulting your health care provider. Be careful with any conditions that may lead to a drop in blood pressure (such as diar- rhea, sweating, vomiting, dehydration); if light-headedness or dizziness occurs, consult your health care provider. Avoid over the counter drugs, especially cough, cold, allergy medications. If you need one of these, consult your health care provider. You may experience these side effects: GI upset, loss of appetite, change in taste percep- tion (limited effects; if they persist or become a problem, consult your health care provider); mouth sores (frequent mouth care may help); rash; fast heart rate; dizziness, light-headedness (passes after a few days of therapy; if it occurs, change position slowly and limit activities requiring alertness and precision); cough. Report mouth sores; sore throat, fever, chills; swelling of the hands, feet; irregular heart- beat, chest pains; swelling of the face, eyes, lips, tongue; difficulty breathing. Representative drugs
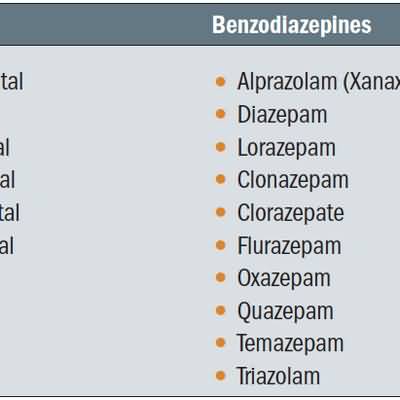
benazepril captopril enalapril enalaprilat fosinopril lisinopril moexipril perindopril quinapril ramipril trandolapril