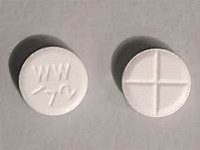
naratriptan

CLINICAL USE
5HT1 receptor agonist:Acute treatment of migraineDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
2.5 mg. Dose may be repeated after 4 hours; maximum 5 mg/24 hoursPHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
OralRate of Administration
–Comments
–OTHER INFORMATION
Do not take second dose at 4 hours during an attack if the first dose was ineffectualNaratriptan is excreted by glomerular filtration and active secretion into the renal tubulesInactive metabolites are renally excreted Studies in patients with impaired renal function (GFR=18–115 mL/min) showed an 80% increase in half-life and a 50% decrease in clearance compared with matched individuals with normal renal function.
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home