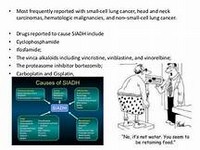
Propofol

CLINICAL USE
Induction and maintenance of general anaesthesiaSedation of ventilated patients for up to 3 daysDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
Induction: 1.5–2.5 mg/kg at a rate of 20–40 mg every 10 secondsMaintenance: 25–50 mg repeated according to response or 4–12 mg/kg/hourSedation: 0.3–4 mg/kg/hour Sedation for surgical and diagnostic procedures: 0.5–1 mg/kg over 1–5 minutes then maintenance: 1.5–4.5 mg/kg/hour orPHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsAdrenergic-neurone blockers: enhanced hypotensive effectAntihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effectADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
IVRate of Administration
See local protocolsComments
–.
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home