Pregabalin

CLINICAL USE
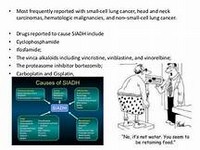
Anti-epileptic agent Neuropathic pain Generalised anxiety disorderDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
150–600 mg daily in 2 or 3 divided dosesPHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
30–60 Initial dose 75 mg daily and titrate according to tolerability and response15–30 Initial dose 25–50 mg daily and titrate according to tolerability and response<15 Initial dose 25 mg daily and titrate according to tolerability and responseDOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
OralRate of Administration
–Comments
–OTHER INFORMATION
Oral bioavailability >90% 50% of dose is removed after a 4 hour haemodialysis sessionUse with caution in people with severe congestive heart failure. May cause reversible deterioration in renal function.
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home