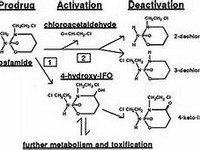
Mirtazapine
CLINICAL USE
Antidepressant
DOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
15–45 mg daily in 1 or 2 divided doses
PHARMACOKINETICS
Molecular weight :265.4 %Protein binding :85 %Excreted unchanged in urine : 75 Volume of distribution (L/kg) :107 litres half-life – normal/ESRD (hrs) :20–40/Increased DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
20 to 50 : Dose as in normal renal function 10 to 20 : Dose as in normal renal function <10 : Start at low dose and monitor closely DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
CAPD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/min HD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/minHDF/high flux :Unknown dialysability. Dose as in GFR <10 mL/minCAV/VVHD :Unlikely to be dialysed. Dose as in GFR 10 to 20 mL/min IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsAlcohol: increased sedative effect Antidepressants: CNS excitation and hypertension with MAOI and moclobemide – avoid concomitant useAntimalarials: avoid concomitant use with artemether and lumefantrineSibutramine: increased risk of CNS toxicity – avoid concomitant use ADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
– Route
Oral Rate of Administration
–Comments
–.
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home