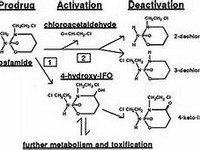
Meropenem
CLINICAL USE
Antibacterial agentDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
500 mg – 1 g every 8 hoursHigher doses used in cystic fibrosis and meningitis (up to 2 g every 8 hours)PHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsProbenecid: avoid concomitant useADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
Add 5 mL water for injection to each 250 mg of meropenemRoute
IVRate of Administration
Bolus: 5 minutes IV Infusion: 15–30 minutesComments
Further dilute in 50–200 mL sodium chloride 0.9%, glucose 5% or glucose 10% if for infusionStable for 24 hours once reconstituted Minimum volume 1 g in 10 mL. (UK Critical Care Group, Minimum Infusion Volumes for fluid restricted critically ill patients, 3 rd Edition, 2006)OTHER INFORMATION
Metabolite is inactive and renally excreted Each 1 g vial contains 3.9 mmol of sodium Has less potential to induce seizures than imipenemHas been used intraperitoneally for peritoneal dialysis Pseudomonas peritonitis at concentration of 100 mg/L50% is removed by CVVHF, 13–53% by CVVHDF, 50% by intermittent
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home