Exenatide

Exenatide
CLINICAL USE
Adjunctive therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitusDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
5–10 mcg twice daily within 60 minutes before the morning and evening mealPHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
30–50 Increase dose to 10 mcg with caution10–30 Avoid. See ‘Other Information’DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
SCRate of Administration
–Comments
–OTHER INFORMATION
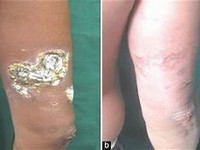
Clearance is reduced by 84% in patients with established renal failureIncreased gastrointestinal side effects in patients with severe renal impairment and on dialysisMay cause renal failure including proteinuria. Avoid in patients with pre-existing renal impairment
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home