Cooking with the right temperatures and times is crucial for achieving flavorful and safe dishes. Effectively controlling heat can significantly improve the texture, taste, and overall quality of your meals. In this post, we will explore the significance of cooking temperatures, how different ranges affect your food, and the issues that can arise when these guidelines are not followed.
The Importance of Cooking Temperatures and Times
Cooking is an art form that also relies heavily on scientific principles. Understanding the correct temperatures and cooking times for various ingredients is essential for the following reasons:
- Ensuring food safety by eliminating harmful bacteria and pathogens.
- Achieving the desired textures and flavors by applying the appropriate heat levels.
- Enhancing consistency and reproducibility in your cooking.
How Different Temperatures Affect the Texture and Flavor of Food
Temperature is fundamental in determining the final outcome of your dish. Here’s how different temperature ranges impact your food:
- Low Temperatures: Slow cooking at low temperatures allows flavors to meld and develop gradually, resulting in tender and flavorful dishes such as stews and braises.
- Medium Temperatures: Cooking at medium heat is ideal for day-to-day meals, ensuring even doneness while retaining moisture without burning the food.
- High Temperatures: High heat is perfect for searing meat to lock in juices, achieving crispy textures, and quickly cooking vegetables while keeping their crunch.
Consequences of Incorrect Cooking Times and Temperatures

Incorrect cooking can lead to disappointing and sometimes unsafe results. Common problems include:
- Under-cooking, which can pose health risks by leaving harmful bacteria in the food.
- Over-cooking, which results in dry, tough textures and diminished flavors.
- Inconsistent cooking, where some parts of the dish are undercooked while others are overdone.
Understanding cooking temperatures and times is vital for culinary success. It requires a balance of safety, flavor, and texture to create dishes that not only taste great but are also enjoyable to eat. By focusing on the appropriate heat levels and cooking durations for each ingredient, you can significantly improve your cooking skills and consistently satisfy your taste buds.
Breaking Down the Science Behind Cooking
How Heat Transfer Works: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
The science of cooking begins with understanding the various methods of heat transfer, which includes conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction: This is the heat transfer method that takes place through direct contact. For example, when you place a steak on a hot grill, the heat from the grill grates transfers directly to the steak, cooking it evenly from the outside in.
- Convection: This involves transferring heat through a fluid medium, such as air or liquid. Baking is a great example, where the hot air in the oven circulates around the food, cooking it evenly.
- Radiation: This method uses electromagnetic waves to transfer heat. For instance, when using a microwave oven, microwaves penetrate the food, causing water molecules to vibrate and generate heat.
The Role of Room Temperature Ingredients in Cooking
Starting with ingredients at room temperature can significantly influence your cooking results. When items like meats, eggs, or dairy are used straight from the refrigerator, they can take longer to cook or may cook unevenly. Here’s why room temperature matters:
- Even Cooking: Room temperature ingredients cook more evenly, leading to better texture and flavor.
- Improved Flavor: Cold ingredients can disrupt the cooking process, potentially resulting in undercooked or overcooked sections that affect the overall taste.
- Better Baking: In baking, room temperature ingredients such as butter and eggs combine more smoothly, ensuring a consistent texture in batters and doughs.
How Different Cooking Methods Impact Heat Transfer
Your choice of cooking method can significantly impact how heat is transferred to your food, ultimately affecting cooking times and results. Here’s a look at some common cooking methods:
- Grilling: Cooking over a direct flame uses conduction and radiation. This method is quick and adds a unique smoky flavor.
- Baking: Using an oven, this method relies on convection as hot air circulates to cook food evenly, perfect for everything from cakes to casseroles.
- Boiling: Here, food is submerged in hot water, with convection currents helping to cook it quickly and uniformly.
- Frying: Heat is transferred through the oil (conduction), resulting in crispy textures and quick cooking. However, close monitoring is necessary to avoid burning.
Understanding how heat transfer works and the importance of starting with room temperature ingredients can greatly enhance your cooking outcomes. By selecting the right method for your dish and preparing ingredients properly, you can achieve consistent and delicious results every time.
Cooking Times and Temperatures for Various Food Elements

Knowing the proper cooking times and temperatures for different foods is essential for both delicious meals and safe consumption. Let’s take a closer look at specifics for meats, vegetables, grains, legumes, and dairy products.
Meat: Recommended Temperatures
Cooking meat to the correct temperature is crucial for eliminating harmful bacteria while achieving optimal flavor and texture. Here are recommended temperatures for various meats:
- Beef: Ground beef should be cooked to an internal temperature of 160°F (71°C), while steaks and roasts should reach at least 145°F (63°C) with a resting time of three minutes.
- Pork: Ground pork should also reach 160°F (71°C). Whole cuts like chops and roasts are safe at 145°F (63°C), followed by a three-minute rest.
- Chicken: Poultry should always be cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to ensure all harmful bacteria are eliminated.
- Fish: Fish should be cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) and is done when it becomes opaque and flakes easily.
Vegetables: Ideal Cooking Times and Methods
Vegetables retain the most nutrients and best taste when cooked properly. Here are some guidelines:
- Broccoli: Steam for 5-7 minutes until bright green and tender-crisp.
- Carrots: Roast at 425°F (218°C) for 20-25 minutes to enhance their natural sweetness.
- Green Beans: Blanch in boiling water for 3-5 minutes, then immerse in ice water to halt cooking and retain color.
- Potatoes: Boil or steam for 15-20 minutes until easily pierced with a fork, or roast at 400°F (204°C) for 30-40 minutes.
Grains and Legumes: Perfecting the Cooking Process
Grains and legumes require precise cooking methods to avoid being undercooked or overcooked:
- Rice: Simmer on low heat for 18-20 minutes for white rice and 40-45 minutes for brown rice.
- Quinoa: Rinse thoroughly before cooking. Simmer for approximately 15 minutes until water is absorbed and it becomes fluffy.
- Lentils: Depending on the variety, simmer for 15-20 minutes (green/brown) or 20-30 minutes (red/yellow).
- Beans: Dried beans should be soaked overnight and then simmered for 1-2 hours, depending on the variety, until tender.
Dairy Products: Key Considerations for Cooking
Dairy products must be cooked carefully to prevent curdling or burning:
- Milk: Heat slowly over medium heat and avoid boiling to prevent scorching.
- Cheese: Melt over low heat to maintain a smooth texture; high heat can cause graininess.
- Yogurt: Use in recipes at or below 375°F (190°C) to avoid curdling; many dishes add it toward the end of cooking.
- Butter: Melt over low to medium heat; for clarified butter, simmer to remove milk solids and water.
By following these guidelines for cooking times and temperatures, you can ensure that your meals are both delicious and safe to eat.
Ensuring Food Safety Through Proper Cooking
Using Food Thermometers to Verify Safe Temperatures
One of the most effective methods to ensure your food is safely cooked is by using a food thermometer. This tool allows you to accurately check the internal temperature of dishes, ensuring harmful bacteria are eliminated. When using a food thermometer, follow these steps:
- Insert the thermometer into the thickest part of the meat without touching bone, fat, or gristle.
- Wait for the temperature to stabilize, and check if it meets the recommended safety temperature.
- For poultry, aim for 165°F (74°C); for ground meats, 160°F (71°C); and for whole cuts of meat, 145°F (63°C).
By using a food thermometer regularly, you can prevent undercooking and lower the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Understanding the Danger Zone for Bacterial Growth
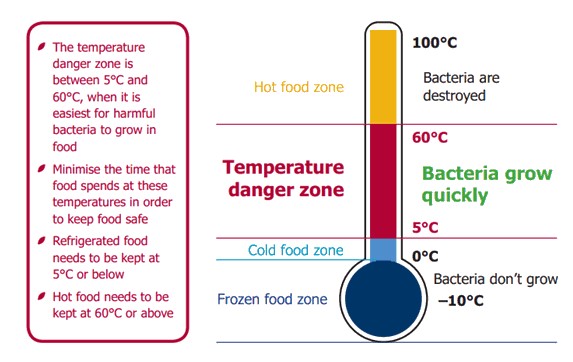
An important aspect of food safety is recognizing the “danger zone” where bacteria thrive. The danger zone temperature range is between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C). Within this range, bacteria can multiply rapidly, increasing the risk of contamination. Here are key points to remember:
- Keep hot food hot (above 140°F) and cold food cold (below 40°F).
- Avoid leaving perishable foods out for more than two hours.
- Refrigerate or freeze leftovers promptly to prevent bacterial growth.
Being aware of the danger zone helps maintain food safety and minimizes health risks.
Safe Food Handling Practices and Techniques
In addition to monitoring cooking temperatures and avoiding the danger zone, proper food handling practices are essential for food safety. Here are some key techniques to follow:
- Handwashing: Always wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before and after handling food.
- Cross-contamination Prevention: Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw meats, vegetables, and ready-to-eat foods.
- Proper Storage: Store raw meats in sealed containers on the lowest shelves of the refrigerator to prevent juices from dripping onto other foods.
- Thawing Food Safely: Thaw frozen foods in the refrigerator, in cold water, or in the microwave rather than at room temperature.
By adhering to these safe food handling practices, you reduce the risk of contamination and ensure that your meals are safe and healthy.
Quick Reference Guide for Cooking Times and Temperatures
A Concise Guide to Cooking Times and Temperatures
Cooking times and temperatures are vital for achieving the best results in any recipe. To assist you in the kitchen, we’ve created an easy reference chart with recommended cooking times and temperatures for a variety of common foods.
Recommended Cooking Times and Temperatures Chart
- Chicken: 165°F (74°C) internal temperature, 20-30 minutes per pound
- Beef (steak): 145°F (63°C) for medium-rare, 160°F (71°C) for medium, 4-6 minutes per side
- Pork: 145°F (63°C) internal temperature, 25-30 minutes per pound
- Fish: 145°F (63°C) internal temperature, 10 minutes per inch of thickness
- Vegetables: 400°F (200°C), 20-25 minutes
Tips for Using the Reference Guide in the Kitchen
Utilizing a reference guide can enhance your time in the kitchen. Here are some tips on how to get the most from it:
- Keep it accessible: Place the guide somewhere easy to reach, like on your fridge or a kitchen cabinet.
- Use a meat thermometer: Always check the internal temperature of meats to ensure doneness.
- Adjust for your oven: Keep in mind that cooking times may vary based on your specific oven, so monitor your food closely.
- Note personal preferences: Tweak the times slightly based on your taste preferences and desired textures.
Importance of Following the Guide for Culinary Success
Following recommended cooking times and temperatures is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Properly cooked food ensures that harmful bacteria are eliminated, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Flavor: Achieving the correct temperature guarantees that food cooks evenly, enhancing its natural flavor.
- Texture: Cooking within the recommended guidelines helps maintain ideal textures, making your meals more enjoyable.
- Consistency: Sticking to consistent methods helps achieve repeatable results, ensuring your dishes are reliably delicious every time.
With this quick reference guide, you can confidently navigate your way through various recipes, ensuring excellent cooking results each time you step into the kitchen.

