MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
FOODS THAT HEAL
FOODS TO LIMIT
WHO’S AFFECTED
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease of the central nervous system that most often strikes people between the ages of 20 and 40
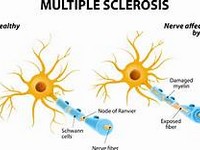
MS is characterized by the gradual destruction of the myelin sheaths that insulate the nerve fibers, thus robbing nerves of the ability to transmit impulses
Although the symptoms vary depending on the sites where myelin is destroyed in the brain and spinal cord, most people suffer abnormal fatigue, impaired vision, slurred speech, loss of balance and muscle coordination, difficulty chewing and swallowing, tremors, bladder and bowel problems, and, in severe cases, paralysis
Nutrition Connection
The main role of diet for those with MS is to help control symptoms such as fatigue, constipation, urinary tract infections, and problems with chewing and swallowingHere are guidelines to discuss with your doctor or dietician: Think low-fat, high-fiber
A low-fat, high-fiber diet that contains fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can be helpful in managing MS by providing energy and nutrients to maintain and repair tissues, to fight infections, and to keep the risk of constipation low
Some foods include prune juice, bran cereal, raspberries, strawberries, whole wheat pastas, whole grain breads and cereals, barley, bran flakes, split peas, lentils, artichokes, peas, and broccoli
Eat foods rich in antioxidants
Some scientists believe that free radical damage can promote the progression of MS
Antioxidants are believed to counter the effect of these free radicals, so it is prudent to include antioxidant-rich foods in your daily diet
These include fruits and vegetables for vitamin C and beta-carotene, such as oranges, carrots and papaya; vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds for vitamin E; and whole grains, nuts, and seafood for selenium
Get plenty of vitamin D
Some studies suggest that vitamin D might prevent progression of the disease or may play other protective roles
In addition, people with MS are at risk for osteoporosis, and vitamin D plays an important role in lowering this risk
Good food sources include milk, fortified soy and rice beverages, fatty fish, and margarine
Increase fluid intake
Constipation is aggravated by an inadequate fluid intake
Also, urinary tract infections are often a problem for people with MS, particularly when they have to undergo frequent catheterizations
Drinking cranberry juice may help by increasing urinary acidity and creating a hostile environment for bacteria
QUICK TIP:
Regulate your tempHeat worsens multiple sclerosis symptoms in many people, so make sure your air conditioners are working well in summer, avoid hot tubs, and choose swimming pools that aren’t kept too warm
Avoid caffeine
If urinary incontinence is a problem, people with MS should avoid caffeinated drinks, such as coffee, tea, and colas, and save chocolate (it also contains caffeine) for an occasional treat
Caffeine has a diuretic effect and irritates the bladder
Eat small, frequent meals
This helps to provide a constant source of energy
Don’t skip breakfast
A nutritious breakfast provides an important energy boost to start the day
Avoid problem foods
Some people with MS have problems with bowel incontinence, which may be worsened by diet
Try eliminating suspect items such as coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods from the diet for a few days; then reintroduce them one at a time to see if the problem recurs
Be careful with food textures
Modify food preparations to address difficulties with chewing and swallowing
For example, substitute shakes, yogurt, fruit and vegetable purees, thick soups, and puddings for firm or dry dishes
Be wary of unproven diets
Some physicians as well as MS support groups advocate the Swank diet (named for the professor who proposed it in 1950), which eliminates most animal fats
This diet was evaluated for many years, with inconclusive results
Other diets that have been proposed for treating MS are riskier, because they may lead to unbalanced or inadequate nutrition
Among them are liquid diets, crash diets, raw food diets, diets that restrict intake of pectin and fructose, and gluten- free regimens
None of these have been proven effective
Look into vitamin therapy
Vitamin therapy has been promoted as helpful for people with MS
Studies suggest that vitamin D may lower the risk of developing MS
Your doctor can help determine the right dosage for you
200 new cases of multiple sclerosis are diagnosed each week in the US
WHO’S AFFECTED
Beyond the Diet
Although there is no cure, and living with MS can be difficult, these lifestyle adjustments may help to manage MS a little easier: Don’t smokeMS sufferers often experience diarrhea or incontinence
Because nicotine can (among many other health effects) stimulate the bowel, which worsens these symptoms, it is important not to smoke
Exercise
For those with mild to moderate MS, regular aerobic exercise can improve strength, muscle tone, balance, and coordination
It also helps relieve stress and symptoms of depression
Rest
Address fatigue by getting plenty of sleep at night
Watch your weight
It is especially important to maintain an appropriate weight related to height
Excess weight can add to mobility problems and can fatigue and strain the respiratory and circulatory systems
Being underweight is also undesirable, because it may decrease resistance to infection and increase the risk of developing pressure sores and other skin ulcers
Seek emotional support
Stay connected to your friends and family, and talk to your doctor who may be able to recommend a therapist, counselor, or support group in your area for those dealing with MS
Importance of well balance diet




