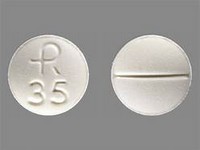
Ethambutol hydrochloride
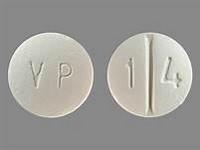
Ethambutol hydrochloride
CLINICAL USE
Antibacterial agent:TuberculosisDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
15 mg/kg/day or 30 mg/kg 3 times a week (supervised dosing)PHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
OralRate of Administration
–Comments
–OTHER INFORMATION
Monitor plasma levels. Dosages should be individually determined and adjusted according to measured levels and renal replacement therapyPeak levels are taken 2–2.5 hours post dose (2–6 mg/L or 7–22 micromol/L); trough is taken pre dose (<1 mg/L or <4 micromol/L)Baseline visual acuity tests should be performed prior to initiating ethambutolDaily dosing is preferred by some specialists to aid compliance and ensure maximum therapeutic effect
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home