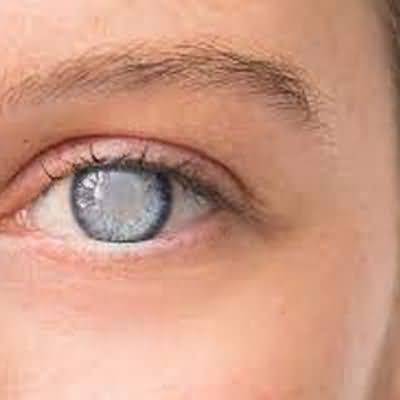
ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSISGradually progressive blurred vision
No pain or redness
Lens opacities (may be grossly visible)
General Considerations
Cataracts are opacities of the crystalline lens and are usually bilateral
They are the leading cause of blindness worldwide
Age-related cataract is by far the most common cause
Other causes includecongenital (owing to intrauterine infections, such as rubella and CMV, or inborn errors of metabolism, such as galactosemia)traumaticsecondary to systemic disease (diabetes mellitus, myotonic dystrophy, atopic dermatitis)topical, systemic or inhaled corticosteroid treatmentradiation exposure
Most persons over age 60 have some degree of lens opacity
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of cataract formation
Multivitamin/mineral supplements and high dietary antioxidants may prevent the development of age-related cataract
Clinical Findings
The predominant symptom is progressive blurring of vision
Glare, especially in bright light or when driving at night; change of focusing, particularly development of nearsightedness; and monocular double vision may also occur
Even in its early stages, a cataract can be seen through a dilated pupil with an ophthalmoscope or slit lamp
As the cataract matures, the retina will become increasingly difficult to visualize, until finally the fundus reflection is absent and the pupil is white
Treatment
Functional visual impairment, specifically its effect on daily activities such as increased falls, is the prime criterion for surgery
The cataract is usually removed by one of the techniques in which the posterior lens capsule remains (extracapsular), thus providing support for a prosthetic intraocular lens
Laser treatment may be used during surgery and may be required subsequently if the posterior capsule opacifies
Ultrasonic fragmentation (phacoemulsification) of the lens nucleus and foldable intraocular lenses allow cataract surgery to be performed through a small incision without the need for sutures, thus reducing the postoperative complication rate and accelerating visual rehabilitation
Multifocal and accommodative intraocular lenses reduce the need for both distance and near vision correction
In the developing world, manual small-incision surgery, in which the lens nucleus is removed intact, is popular because less equipment is required
Prognosis
Cataract surgery is cost-effective in improving survival and quality of life
In the developed world, it improves visual acuity in 95% of cases
In the other 5%, there is preexisting retinal damage or operative or postoperative complica- tions
In less developed areas, the improvement in visual acuity is not as high, in part due to uncorrected refractive error postoperatively
A large number of drugs, such as alpha-1-antagonists for benign prostatic hyperplasia or systemic hypertension and antipsychotics, increase the risk of complications during surgery (floppy iris syndrome) and in the early postoperative period
Stopping the drug for 1–2 weeks prior to surgery may be beneficial
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction increases the risk of intraocular infection (endophthalmitis)
When to Refer
Patients with cataracts should be referred to an ophthalmologist when their visual impairment adversely affects their everyday activities
Loss of vision in one eye that is usually rapid, possibly with “curtain” spreading across field of vision
No pain or redness
Detachment seen by ophthalmoscopy
General Considerations
Most cases of retinal detachment are due to development of one or more peripheral retinal tears or holes (rhegmatogenous retinal detachment)
This is usually spontaneous, related to degenerative changes in the vitreous, and generally occurs in persons over 50 years of age
Nearsightedness and cataract extraction are the two most common predisposing causes
It may also be caused by penetrating or blunt ocular trauma
Tractional retinal detachment occurs when there is preretinal fibrosis, such as in proliferative retinopathy due to diabetic retinopathy or retinal vein occlusion or as a complication of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment
Exudative retinal detachment results from accumulation of subretinal fluid, such as in neovascular age-related macular degeneration or secondary to choroidal tumor
Clinical Findings
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment usually starts in the superior temporal area, spreading rapidly to cause visual field loss that starts inferiorly and expands upward
Premonitory symptoms of the predisposing vitreous degeneration and vitreo-retinal traction are recent onset of or increase in floaters (moving spots or streaks in the visual field) and photopsias (flashes of light)
Central vision remains intact until the macula becomes detached
On ophthalmoscopic examination, the retina is seen hanging in the vitreous like a gray cloud (Figure 7–3)
One or more retinal tears or holes will usually be found on further examination
In traction retinal detachment, there is irregular retinal elevation
In exudative retinal detachment, the retina is dome-shaped and the subretinal fluid shifts position with changes in posture
Ocular ultrasonography assists the detection and characterization of retinal detachment
Treatment
Treatment of rhegmatogenous retinal detachments is directed at closing all of the retinal tears and holes by forming a permanent adhesion between the neurosensory ret- ina, the retinal pigment epithelium, and the choroid with laser photocoagulation to the retina or cryotherapy to the sclera
The following may be required to achieve apposition of the neurosensory retina to the retinal pigment epithelium while the adhesion is developing: indentation of the sclera with a silicone sponge or buckle, subretinal fluid drainage via an incision in the sclera, or injection of anexpansile gas or silicone oil into the vitreous cavity following intraocular surgery to remove the vitreous (pars plana vitrectomy)
Certain types of uncomplicated retinal detachment may be treated by pneumatic retinopexy, in which an expansile gas is injected into the vitreous cavity followed by positioning of the patient’s head to facilitate reattachment of the retina
Once the retina is repositioned, the defects are sealed by laser photocoagulation or cryotherapy; these two methods are also used to seal retinal defects without associated detachment
In complicated retinal detachments, particularly traction retinal detachments, retinal reattachment can be accomplished only by pars plana vitrectomy, direct manipulation of the retina, and internal tamponade of the retina with air, expansile gas, or silicone oil
(The presence of an expansile gas within the eye is a contraindication to air travel, mountaineering at high altitude, and nitrous oxide anesthesia
Such gases persist in the globe for weeks after surgery
)
Treatment
of exudative retinal detachments is determined by the underlying cause
Prognosis
About 90% of uncomplicated rhegmatogenous retinal detachments can be cured with one operation
The visual prognosis is worse if the macula is detached or if the detachment is of long duration
When to Refer
All cases of retinal detachment must be referred urgently to an ophthalmologist, emergently if central vision is good because this indicates that the macula has not detached
During transportation, the patient’s head is positioned so that the detached portion of the retina will fall back with the aid of gravity